Figure 27 : Example to Solve quaint equation F(x)=0
Product no. Program 17 05
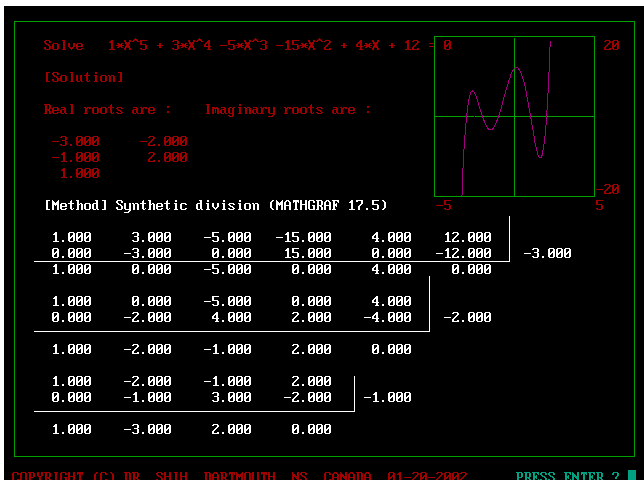
Q1. This diagram can be used to solve
-
1. x^5 + 3*x^4 - 5*x^3 - 15*x^2 + 4*x + 12 = 0
2. x^5 + 3*x^4 - 5*x^3 - 15*x^2 + 4*x + 12 > 0. See Q2
3. x^5 + 3*x^4 - 5*x^3 - 15*x^2 + 4*x + 12 < 0. See Q3
Q2. Solve y = x^5 + 3*x^4 - 5*x^3 - 15*x^2 + 4*x + 12 > 0
A2. From diagram we have y = (x+3)*(x+2)*(x+1)*(x-1)*(x-2)
- If x < -3,
- x+3=(-), (x+2)=(-), (x+1)=(-), (x-1)=(-), (x-2)=(-)
- Hence y < 0 when x < -3 is not an answer
- x+3=(-), (x+2)=(-), (x+1)=(-), (x-1)=(-), (x-2)=(-)
- if -3 < x < -2,
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(-), (x+1)=(-), (x-1)=(-), (x-2)=(-)
- Hence y > 0 when -3 < x < -2 is an answer
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(-), (x+1)=(-), (x-1)=(-), (x-2)=(-)
- if -2 < x < -1,
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(+), (x+1)=(-), (x-1)=(-), (x-2)=(-)
- Hence y < 0 when -2 < x < -1 is not an answer
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(+), (x+1)=(-), (x-1)=(-), (x-2)=(-)
- if -1 < x < 1,
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(+), (x+1)=(+), (x-1)=(-), (x-2)=(-)
- Hence y > 0 when -1 < x < 1 is an answer
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(+), (x+1)=(+), (x-1)=(-), (x-2)=(-)
- if 1 < x < 2,
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(+), (x+1)=(+), (x-1)=(+), (x-2)=(-)
- Hence y < 0 when 1 < x < 2 is not an answer
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(+), (x+1)=(+), (x-1)=(+), (x-2)=(-)
- if x > 2,
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(+), (x+1)=(+), (x-1)=(+), (x-2)=(+)
- Hence y > 0 when x > 2 is an answer
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(+), (x+1)=(+), (x-1)=(+), (x-2)=(+)
Q3. Solve y = x^5 + 3*x^4 - 5*x^3 - 15*x^2 + 4*x + 12 < 0
A3. From diagram we have y = F(x) = (x+3)*(x+2)*(x+1)*(x-1)*(x-2)
- If x < -3,
- x+3=(-), (x+2)=(-), (x+1)=(-), (x-1)=(-), (x-2)=(-)
- Hence y < 0 when x < -3 is an answer
- x+3=(-), (x+2)=(-), (x+1)=(-), (x-1)=(-), (x-2)=(-)
- if -3 < x < -2,
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(-), (x+1)=(-), (x-1)=(-), (x-2)=(-)
- Hence y > 0 when -3 < x < -2 is not an answer
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(-), (x+1)=(-), (x-1)=(-), (x-2)=(-)
- if -2 < x < -1,
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(+), (x+1)=(-), (x-1)=(-), (x-2)=(-)
- Hence y < 0 when -2 < x < -1 is an answer
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(+), (x+1)=(-), (x-1)=(-), (x-2)=(-)
- if -1 < x < 1,
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(+), (x+1)=(+), (x-1)=(-), (x-2)=(-)
- Hence y > 0 when -1 < x < 1 is not an answer
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(+), (x+1)=(+), (x-1)=(-), (x-2)=(-)
- if 1 < x < 2,
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(+), (x+1)=(+), (x-1)=(+), (x-2)=(-)
- Hence y < 0 when 1 < x < 2 is an answer
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(+), (x+1)=(+), (x-1)=(+), (x-2)=(-)
- if x > 2,
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(+), (x+1)=(+), (x-1)=(+), (x-2)=(+)
- Hence y > 0 when x > 2 is not an answer
- x+3=(+), (x+2)=(+), (x+1)=(+), (x-1)=(+), (x-2)=(+)
We can also write as below to find F(x) < 0
-
...... -3 < x .. -3 < x < -2 .. -2 < x < -1 .. -1 < x < 1 .. 1 < x < 2 .. X > 2
(x+3) ... - ......... + ............ + ............ + .......... + ........ +
(x+2) ... - ......... - ............ + ............ + .......... + ........ +
(x+1) ... - ......... - ............ - ............ + .......... + ........ +
(x-1) ... - ......... - ............ - ............ - .......... + ........ +
(x-2) ... - ......... - ............ - ............ - .......... - ........ +
F(x) .... - ......... + ............ - ............ + .......... - ........ +
Q4. Find range of y = x^5 + 3*x^4 - 5*x^3 - 15*x^2 + 4*x + 12
A4. Fow following domain
-
1. When x is between -2 and -1
- The minimum point at x=-1.5022 and y=-3.25
- Hence the range is from -3.25 < y < 0
- The minimum point at x=1.605 and y=-10.335
- Hence the range is from -10.335 < y < 0
Q5. Find F(-1.5022)
- Use MD2002 ZM17 program 09
- Give coefficients : 1, 3, -5, -15, 4, 12
- Give root a+b*i : -1.6022, 0
Q6. Find F(1.605)
- Use MD2002 ZM17 program 09
- Give coefficients : 1, 3, -5, -15, 4, 12 (not required because given in Q5)
- Give root a+b*i : -1.605, 0
Q6. Reference
- Solve quaint equation : MD2002 ZM17 program 05
- Find F(a+b*i) : MD2002 ZM17 program 09