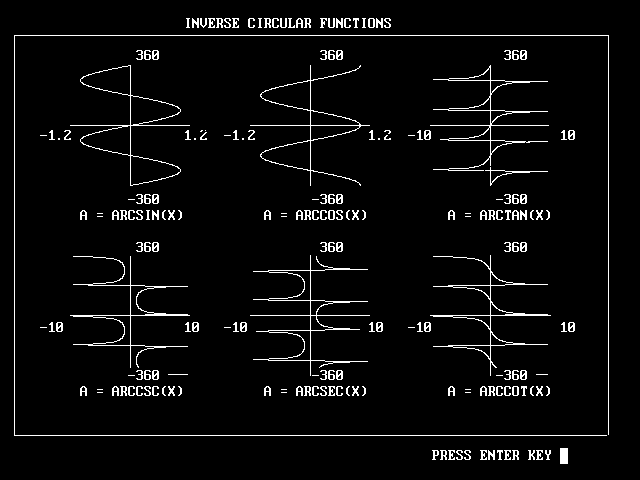
Defintion
- y = arcsin(x) : arcsine curve
- arcsin(1) = 90.
- arcsin(1/2) = 30.
- arcsin(sin(x) = x.
- sin(arcsin(x) = x.
- y = arccos(x) : arccosine curve
- arccos(1) = 0.
- arccos(1/2) = 60.
- arccos(cos(x)) = x.
- cos(arccos(x)) = x.
- y = arctan(x) : arctangent curve.
- arctan(1) = 45.
- arctan(Sqr(3)) = 60.
- arctan(tan(x)) = x.
- tan(arctan(x)) = x.
- y = arccsc(x) : arccscant curve
- arccsc(1) = 90.
- arccsc(2) = 30.
- arccsc(csc(x) = x.
- csc(arccsc(x) = x.
- y = arcsec(x) : arcsecant curve
- arcsec(1) = infinite.
- arcsec(2) = 60.
- arcsec(sec(x)) = x.
- sec(arcsec(x)) = x.
- y = arccot(x) : arccotangent curve.
- arccot(1) = 45.
- arccot(Sqr(3)) = 30.
- arccot(cot(x)) = x.
- cot(arccot(x)) = x.
|