-
Symbol Defintion
x^2 = square of x
Ge 02 01. Bisect a line
Diagram

- Start the diagram program
- Write down the steps to bisect aline
- Bisector is perpendicular to line
- Bisector divides the line to two equal parts
- Point on bisector has has distance from the ends of line
Go to Begin
GE 02 02. Bisector of a angle
Diagram
- Write down step how to bisect an angle
- Bisector is equally dividing the angle
- Point on bisector has has distance from the rays of angle
Go to Begin
GE 02 03. Locus
Diagram
- See GE 02 01
- A point to two fixed points keeps same distance
- What is the locus of the point ?
Go to Begin
GE 02 04. Locus
Diagram
- See GE 02 02
- A point to two fixed rays keeps same distance
- What is the locus of the point ?
Go to Begin
GE 02 05. Bisectors of sides of triangle ABC
Construction
- Draw a large triangle ABC
- Draw bisector of side BC
- Draw bisector of side CA
- Draw bisector of side AB
- Do bisectors meet at one point Q ? If not, try again
- If they meet at point Q
- Measure QA, QB and QC
- Do we have QA = QB = QC ? if not, try again
- If QA = QB = QC, Use Q as center and QA as radius to draw a circle
- The center Q is circum-center
Go to Begin
GE 02 06. Bisectors of angles of triangle ABC
Diagram
- Draw a large triangle ABC
- Draw bisector of angle A
- Draw bisector of angle B
- Draw bisector of angle C
- Do bisectors meet at one point Q ? If not, try again
- If they meet at point Q
- Measure distance from Q to the sides QD, QE, QF
- Do we have QD = QE = QE ? if not, try again
- If QD = QE = QF, Use Q as center and QD as radius to draw a circle
- The center of circle is in-center of triangle
Go to Begin
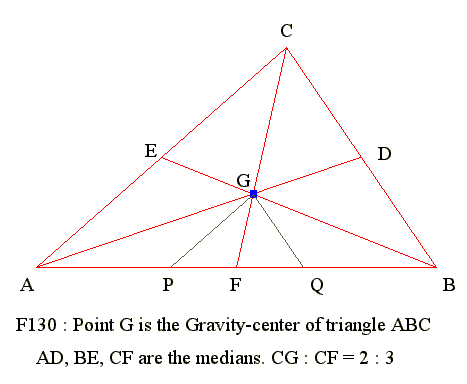
GE 02 07. Medians of triangle
Diagram
- From vertex of triangle draw a line to mid point of opposite side
- Triangle has three medians
- Three medians are concurrent at a point G which is centroid
- AG = 2*(Median AD)/3 where D is the mid point of BC
- Point G is the centroid or gravity center
Go to Begin
GE 02 08. Altitudes of triangle
Diagram
- From vertex of triangle draw a line perpendicular to opposite side
- Triangle has three altitudes
- Three altitudes are concurrent at a point 0 which is ortho-center
- AD, BE, CF are altitudes. D on BC, E on CA and F on AB
- A,B,D,E are concyclic if AB is diameter of a circle
- B,C,E,F are concyclic if BC is diameter of a circle
- C,A,F,D are concyclic if CA is diameter of a circle
Go to Begin
GE 02 09. Lines in a circle
Tangent
- It is line touching the circle only at one point.
- The line is tangent
- Connect two points on circle which is a chord
- Draw a line from a point outside a circle
- The line meets two points on circle
Go to Begin
GE 02 10. Exercises
Home work : By construction method
- 1. Draw three medians of a triangle to find centroid
- 2. Draw three altitudes of a triangle to find ortho-center
- 3. Draw three angle bisectors of a triangle to find in-center
- 4. Draw three side bisectors of a triangle to find circum-center
- 5. Find the distance from in-center to the sides using a ruler
- 6. Find the distance from circum-center to the vertices using a rule
Go to Begin
GE 02 00. Outlines
- Bisector of angle
- Bisector of line
- Bisectors of angle of triangle
- Bisectors of sides of triangle
- Medians of triangle
- Altitudes of triangle
- Chord of a circle
- Tangent of a circle
- Secant of a circle
Go to Begin