Figure 117 : Divide line into 3 equal parts
Q01. Diagram
|
Equilateral triangle - Divide side into 3 equal parts 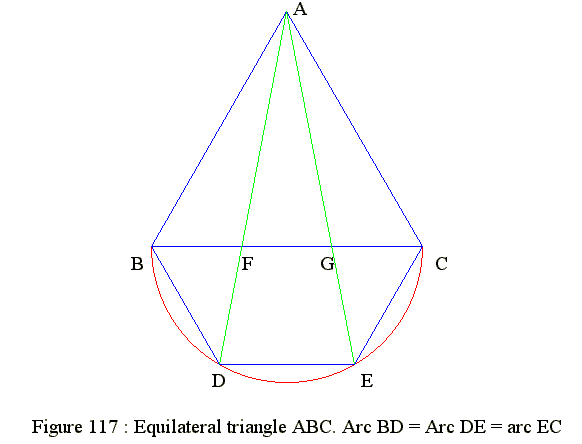
|
Go to Begin
Q02. Equilateral triangle - Divide side into 3 equal parts
Keywords
- Properties of equilateral triangle
- Properties of hexagon
- Law of cosine and law of sine
- Draw an equilateral triangle ABC
- Use BC as diameter to draw a semi-circle below BC with center O
- Divide the semi-circle into 3 equal arcs : Arc BD = arc DE = arc EC
- Join AD and cut BC at F
- Join AE and cut BC at G
- Then BF = FG = GC
- Let BC = AB = 2
- By construction BD is one side of regular hexagon
- Hence BD = 1 and angle FBD = 60
- Hence angle ABD = ABF + FBD = 60 + 60 = 120 degrees
- In triangle ABD, find AD by cosine law
- We know AB = 2, angle ABD = 120 degrees and BD = 1.
- AD^2 = AB^2 + BD^2 - 2*AB*BD*cos(ABD)
- AD^2 = 2^2 + 1^2 - 2*2*1*cos(120)
- AD^2 = 5 - 4*(-1/2)
- AD^2 = 7 or AD = Sqr(7)
- In triangle ABD, we can find angle BAD by sine law
- BD/sin(BAD) = AD/sin(ABD)
- Hence sin(BAD)
- = BD*sin(ABD)/AD
- = 1*sin(120)/Sqr(7)
- = (Sqr(3)/2)/(Sqr(7))
- = Sqr(3)/(2*Sqr(7) ............... (1)
- Use sin(x)^2 + cos(x)^2 = 1, we have
- cos(BAD)
- = Sqr(1 - sin(BAD)^2)
- = Sqr(1 - 3/28)
- = 5/Sqr(28) ...................... (2)
- In right triangle AOF where AO perpendicular to BC, find AF
- AO = Sqr(AB^2 - (BC/2)^2) = Sqr(3)
- Angle FAO = 30 - angle BAF
- cos(FAO) = cos(30 - BAF)
- = cos(30)*cos(BAF) + sin(30)*sin(BAF)
- Substitute (1) and (2) into above expression
- cos(FAO) = (Sqr(3)/2)*(Sqr(25/28)) + (1/2)*(1/(2*Sqr(7))
- = (5*Sqr(3)/(2*Sqr(28)) + 1/(4*Sqr(7))
- = (5 + 1)/(4*Sqr(7))
- = 3/(2*Sqr(7)) ............................. (3)
- Since triangle is right triangle
- hence AF = AO/cos(FAO)
- Substitute (3) into above we have
- AF = (Sqr(3)*2*Sqr(7))/3 = 2*Sqr(21)/3 ..... (4)
- In triangle ABF, we use sine law again to find BF
- BF/sin(BAF) = AF/sin(60)
- Substitute (1) and (4) into above expression
- BF = (1/(2*Sqr(7))*(2*Sqr(21)/3)/(Sqr(3)/2)
- = (2*Sqr(21)/(6*Sqr(7))/(Sqr(3)/2)
- = (4*Sqr(21))/(6*Sqr(21))
- = 2/3
- = BC/3 where we assume BC = 2
Go to Begin
Q03. Formula
- 1. cosine law : a^2 = b^2 + c^2 - 2*b*c*cos(A)
- 2. sine law : a/sin(A) = b/sin(B) = c/sin(C) = 2*R
Go to Begin
Q04. Other method : Divide line AB into 3 equal parts
- 1. Draw line AB
- 2. Draw line AC
- 3. Produce AC to D and let CD = AC
- 4. Produce AD to E and let DE = AC
- 5. Join BE
- 6. Draw line DP parallel to BE
- 7. Draw line CQ parallel to BE
- 8. Then AP = PQ = QB
Go to Begin