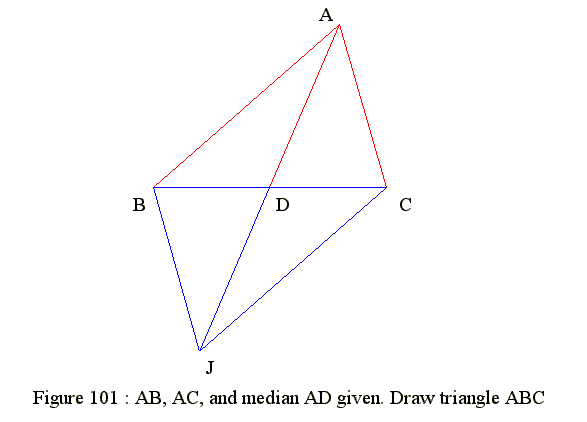
Figure 101 : Sides AB, AC and Median AD are given
- Geometry GE 27 01
Go to Begin
Q02. Figure 102 : Medians AD, AE and side AB are given

- Geometry GE 27 02
Go to Begin
Figure 103 : Three circles touch each other with same common tangent

- Geometry GE 27 03
Go to Begin
Figure 104 : Square side a and Four sim-circle radius a/2

- Geometry GE 27 04
Go to Begin
Figure 105 : Circle inscribed an equilateral triangle (1)
- Geometry GE 27 05
Go to Begin
Figure 106 : Circle inscribed an equilateral triangle (2)
Diagram
- Geometry GE 27 06
Go to Begin
Figure 107 : Square and equaliteral triangle
Diagram
- Geometry GE 27 07
Go to Begin
Figure 108 : Area of triangle formed by medians of triangle ABC
Diagram
- Geometry GE 27 08
- We should remeber the 1/3 rule
- This diagram is also used to prove that medians are concurrent
Go to Begin
Figure 109 : Heights and medians of equilateal triangle ABC
Diagram
- Geometry GE 27 09
Go to Begin
Figure 110 : Pedal triangle of equilateral triangle ABC
Diagram
- Geometry GE 27 10
Go to Begin
Figure 111 : Ex-central triangle of equilateral triangle
- Geometry GE 27 11
Go to Begin
Figure 112 : Pedal triangle of triangle ABC
Diagram
- Geometry GE 27 12
Go to Begin
Figure 113 : Ex-central triangle of triangle ABC
Diagram
- Geometry GE 27 13
Go to Begin
Figure 114 : Construct 4 congruent triangles using triangle ABC
Diagram
- Geometry GE 27 14
Go to Begin
Figure 115 : Ortho-center, centroid and circum-center are colinear
Diagram
- Geometry GE 27 15
Go to Begin
Figure 116 : cos(A - B) = cos(A)*cos(B) - sin(A)*sin(B)
Diagram
- Geometry GE 27 16
Go to Begin
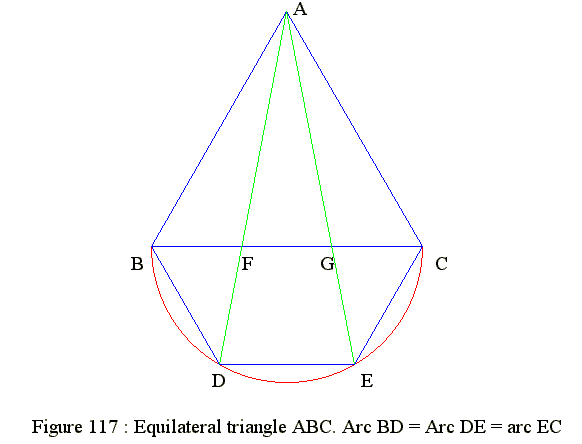
Figure 117 : Divide equilateral triangle side into 3 eqal parts
Diagram
- Geometry GE 27 17
Go to Begin
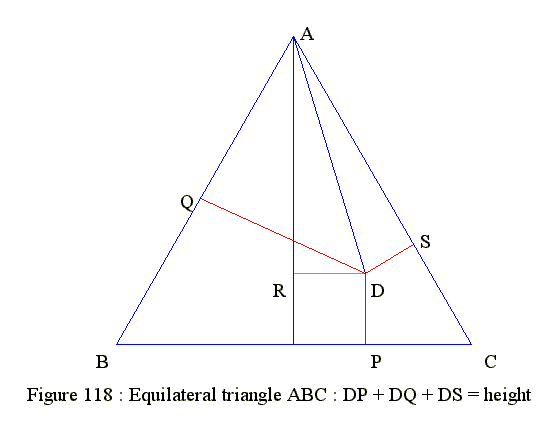
Figure 118 : Point inside equilaleral triangle to sides equal height
Diagram
- Geometry GE 27 18
Go to Begin
Figure 119 : A(7,4), B(3,1), C(0,k) find k if AC + BC is minimum
Diagram
- Geometry GE 27 19
Go to Begin
Figure 120 : Hexagon inscribed equilateral triangle
- Geometry GE 27 20
Go to Begin
Figure 121: Heights are concurrent
Diagram
- Geometry GE 27 21
Go to Begin
Figure 122 : Bisector of a line
Diagram
- Geometry GE 02 01
Go to Begin
Figure 123 : Bisector of an angle
Diagram
- Geometry GE 01 04
Go to Begin
Figure 124 : Conditions of two parallel lines
Diagram
- Geometry GE 01 05
Go to Begin
Figure 125 : Angles in circle
Diagram
- Geometry GE 01 06
Go to Begin
F126 : Trinagle sides s = (a + b + c)/2
Diagram
- 1. Area of triangle = Sqr(s*(s-1)*(s-b)*(s-c))
- 2. In-circle : Tangent at A is (s - a)
- 3. Ex-circle : Tangent at A is s
- 4. Half angle formula in terms of s
Go to Begin
F127 : Circum-center
Diagram
- GE 02 05
- GE 03 02
Go to Begin
F128 : In-center
Diagram
- GE 02 06
- GE 03 02
Go to Begin
F129 : Ex-center
Diagram
- GE 04 08
Go to Begin
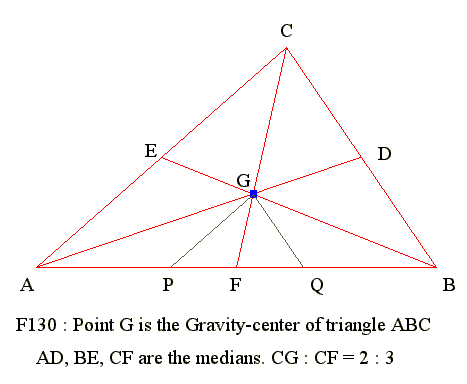
F130 : Centroid
Diagram
- GE 02 07
- GE 03 02
Go to Begin
F131 : Ortho-center
Diagram
- GE 02 08
- GE 03 02
Go to Begin
F132 : Pedal triangle
Diagram
- GE 03 04
- See F112
Go to Begin
F133 : Ex-central triangle
Diagram
- See F113
Go to Begin
F134 : Three points define a circle
Diagram
- GE 04 03
Go to Begin
F135 : Tangent to circle (1)
Diagram
- GE 04 02
Go to Begin
F136 : Tangent to circle (2)
Diagram
- GE 04 02
Go to Begin
F137 : Concyclic
Diagram
Go to Begin
F138 : How many chords ?
Diagram
- GE 04 05
Go to Begin
F139 : Circile inscribed in quadrilateral
Diagram
- GE 04 06 and GE 04 07
Go to Begin
GE 21 40 : Locus - Examples
Diagram
Go to Begin